DETERMINA EL PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN DE LOS SIGUIENTES PROBLEMAS
EJERCICIO NÚMERO 1:
* LA RECTA QUE PASA POR (-1,5), m= -2/3, Y LA RECTA 4x+y-11= 0.
Y2 - Y1
m= ---------------
X2 - X1
y - 5
- 2/3 = ---------------
x - ( -1 )
y - 5
- 2/3 = ---------------
x + 1
- 2/3 ( x + 1) = y - 5
- 2/3x - 2/3 = y - 5
- 2/3x - 2/3 - y + 5 = 0
- 2/3x + 4 1/3- y = 0 ( -1 )
2/3x + y - 13/3 = 0
2/3x + y - 13/3 = 0
4 x + y - 11 = 0
4 x + y - 11 = 0
y = - 4 x + 11
2/3 x + y - 13/3 = 0
2/3 x + (- 4 x + 11) - 13/3 = 0
2/3 x - 4 x + 11 - 13/3 = 0
- 3 1/3 x + 6 2/3 = 0
- 3 1/3 x = - 6 2/3
- 6 2/3
x = --------------
- 3 1/3
x = 2
4 x + y - 11 = 0
4 ( 2 ) + y - 11 = 0
8 + y - 11 = 0
- 3 + y = 0
y = 3
( 2, 3 )
y - 5
- 2x - 2
----------- = y - 5
3
- 2x - 2 = y - 5 ( 3 )
- 2x - 2 = 3y - 15
- 2x - 3y - 2 + 15 = 0
- 2x - 3y + 13 = 0 ( -1 )
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
( 4x + y - 11 = 0 ) ( - 3 )
--------------------------------------
2x+ 3 y - 13 = 0
- 12x- 3 y + 33 = 0
--------------------------------------
- 10 x + 20 = 0
- 10x = - 20
- 20
x = --------
- 10
x = 2
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
2 ( 2 ) + 3y - 13 = 0
4 + 3y - 13 = 0
3 y - 9 = 0
3 y = 9
9
y = ------
3
y = 3
COMPROBACIÓN
4x + y - 11 = 0
4 ( 2 ) + 3 - 11 = 0
8 + 3 - 11 = 0
11 - 11 = 0
0 = 0
EJERCICIO NÚMERO 2:
5x + 3y - 23 = 0
5x + 3 ( - 11x + 17) -23 = 0
5x - 33x + 51 - 23 = 0
- 28x + 28 = 0
- 28x = - 28
- 28
x = -------
- 28
x = 1
11x + y - 17 = 0
11 ( 1 ) + y - 17 = 0
11 + y - 17 = 0
y - 6 = 0
y = 6
RECTAS QUE PASAN POR UN PUNTO (PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN)
Determinar las rectas del plano que pasan por el punto  .
.
La ecuación de la recta ha de ser, como ya se sabe:
 , luego tendrá que cumplirse:
, luego tendrá que cumplirse:
2x + y - 5 = 0
2 ( - 1 ) + 7 - 5 = 0
- 2 + 7 - 5 = 0
7 - 7 = 0
0 = 0
2/3 x + y - 13/3 = 0
2/3 x + (- 4 x + 11) - 13/3 = 0
2/3 x - 4 x + 11 - 13/3 = 0
- 3 1/3 x + 6 2/3 = 0
- 3 1/3 x = - 6 2/3
- 6 2/3
x = --------------
- 3 1/3
x = 2
4 x + y - 11 = 0
4 ( 2 ) + y - 11 = 0
8 + y - 11 = 0
- 3 + y = 0
y = 3
( 2, 3 )
COMPROBACIÓN
2/3 x + y - 13/3 = 0 4 x + y - 11 = 0
2/3 ( 2) + 3 - 13/3 = 0 4 ( 2 ) + 3 - 11 = 0
4/3 + 3 - 13/ 3 = 0 8 + 3 - 11 = 0
13/3 - 13/ 3 = 0 11 - 11 = 0
0 = 0 0 = 0
* OTRA MANERA DE SOLUCIONAR ESTA ECUACIÓN ES:
Y2 - Y1
m= ---------------
X2 - X1
y - 5
- 2/3 = ---------------
x - (-1)
y - 5
- 2/3 = ---------------
x + 1
- 2/3 ( x + 1) = y - 5
- 2x - 2
----------- = y - 5
3
- 2x - 2 = y - 5 ( 3 )
- 2x - 2 = 3y - 15
- 2x - 3y - 2 + 15 = 0
- 2x - 3y + 13 = 0 ( -1 )
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
( 4x + y - 11 = 0 ) ( - 3 )
--------------------------------------
2x
- 12x
--------------------------------------
- 10 x + 20 = 0
- 10x = - 20
- 20
x = --------
- 10
x = 2
2x + 3y - 13 = 0
2 ( 2 ) + 3y - 13 = 0
4 + 3y - 13 = 0
3 y - 9 = 0
3 y = 9
9
y = ------
3
y = 3
( 2 , 3 )
COMPROBACIÓN
4x + y - 11 = 0
4 ( 2 ) + 3 - 11 = 0
8 + 3 - 11 = 0
11 - 11 = 0
0 = 0
VIDEO: PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN DE DOS RECTAS
EJERCICIO NÚMERO 2:
* DETERMINA LOS PUNTOS DE INTERSECCIÓN DE LAS SIGUIENTES ECUACIONES:
11 x + y -17 = 0 Y 5 x + 3y - 23 = 0
11x + y - 17 = 0
y = - 11x + 17
11 x + y -17 = 0 Y 5 x + 3y - 23 = 0
11x + y - 17 = 0
y = - 11x + 17
5x + 3y - 23 = 0
5x + 3 ( - 11x + 17) -23 = 0
5x - 33x + 51 - 23 = 0
- 28x + 28 = 0
- 28x = - 28
- 28
x = -------
- 28
x = 1
11x + y - 17 = 0
11 ( 1 ) + y - 17 = 0
11 + y - 17 = 0
y - 6 = 0
y = 6
( 1, 6 )
COMPROBACIÓN
11x + y - 17 = 0 5x + 3y - 23 = 0
11 ( 1 ) + 6 - 17 = 0 5 ( 1 ) + 3 ( 6 ) - 23 = 0
11 + 6 - 17 = 0 5 + 18 - 23 = 0
17 - 17 = 0 23 - 23 = 0
0 = 0 0 = 0
0 = 0 0 = 0
RECTAS QUE PASAN POR UN PUNTO (PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN)
 .
.La ecuación de la recta ha de ser, como ya se sabe:
 , luego tendrá que cumplirse:
, luego tendrá que cumplirse:Recta que pasa por dos puntos
Si ha de pasar por dos puntos (x1,y1) y (x2,y2) luego tendrá que cumplirse
agrupando términos:
despejando m:
este valor, m, es el de la pendiente de la recta que pasa por los dos puntos: (x1,y1) y (x2,y2).
Despejando ahora el valor de b de una de las ecuaciones del sistema, por ejemplo de la primera, tenemos:
y sustituyendo m, por su valor ya calculado;
Tenemos las dos incógnitas m y b despejadas, en función de las coordenadas de los dos puntos por los que tienen que pasar, la ecuación general de la recta, con los parámetros ya calculados es:
DETERMINA EL PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN DE LAS SIGUIENTES ECUACIONES.
x + y - 3 = 0 Y 2x + y - 6 = 0
( x + y - 3 = 0 ) ( -1)
2x + y - 6 = 0
-----------------------------------------
- x - y + 3 = 0
2x + y - 6 = 0
-----------------------------------------
x - 3 = 0
x = 3
x + y - 3 = 0
3 + y - 3 = 0
y = 0
( 3 , 0 )
COMPROBACIÓN
2x + y - 6 = 0
2 ( 3 ) + 0 - 6 = 0
6 - 6 = 0y
0 = 0
DETERMINA EL PUNTO DE INTERSECCIÓN DE LAS SIGUIENTES ECUACIONES.
2x + y - 5 = 0 Y 5 x + y - 2 = 0
2x + y - 5 = 0 5x + y - 2 = 0
y = - 2x + 5 y = - 5x + 2
- 2x + 5 = - 5x + 2
- 2x + 5 + 5x - 2 = 0
- 2x + 5x + 5 - 2 = 0
3x + 3 = 0
3x = - 3
- 3
x = ----------
3
x = - 1
5x + y - 2 = 0
5 ( -1 ) + y - 2 = 0
- 5 + y - 2 = 0
y - 7 = 0
y = 7
( - 1 , 7 )
COMPROBACIÓN2x + y - 5 = 0
2 ( - 1 ) + 7 - 5 = 0
- 2 + 7 - 5 = 0
7 - 7 = 0
0 = 0






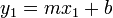
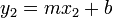






No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario